Kids Dentistry
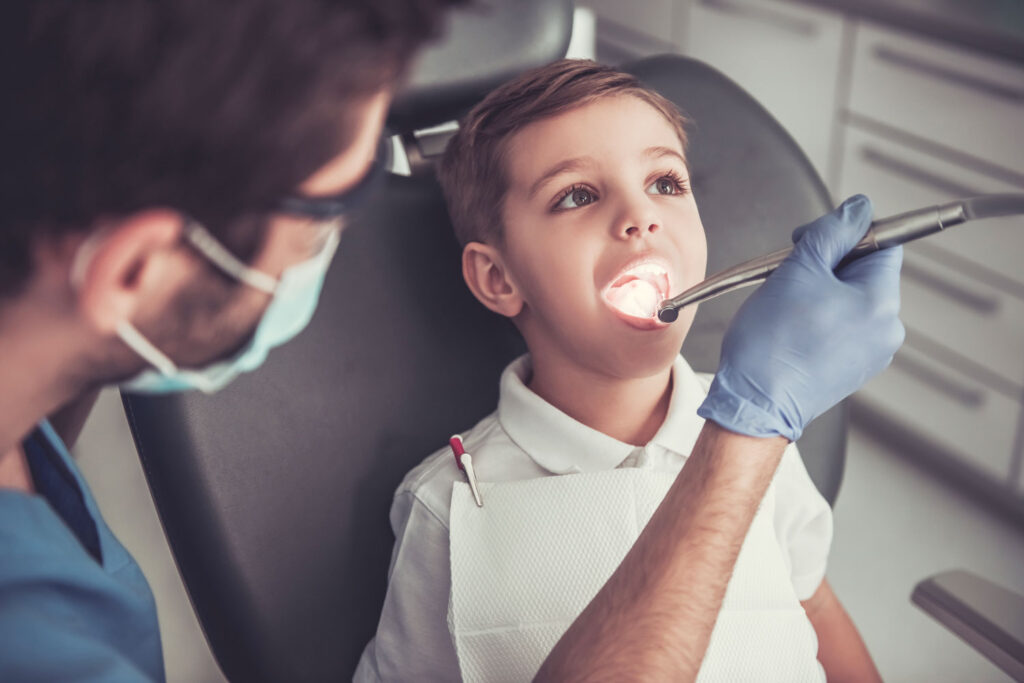
What Is Kids Dentistry?
Kids are special and so are their oral needs. Pediatric Dentistry aims at tailoring dental services to meet the unique needs of growing children. Specialized dentists treating these tiny humans are known as Pedodontists. They provide comprehensive, gentle care in a warm and welcoming environment.
Kids Dentistry differs from general dentistry in several key ways. But more than treatment or instruments, the technique to guide behavior and reduce anxiety is of prime importance.
Why Is Pediatric Dentistry Important?
Humans start teething when they are as young as 6 months old. During the age period from 6 months to 6 years, they develop their set of primary ‘milk’ teeth. By the age of 6-7 years, milk teeth start to fall off and a permanent set of teeth starts to appear in the oral cavity. Milk teeth being temporary, many parents tend to ignore dental visits concerning them. However, they fail to realize the importance of the timeline of milk and permanent teeth in the oral cavity.
Pedodontists (Kids Dentists) ensure proper dental development and long-term oral health.
Why do we need a Kids Specialist?
While General dentists or Children’s Dentists can treat children as well. There are several reasons why visiting a pediatric dental specialist is beneficial:
Specialized Training
Pedodontists dedicate 3+ years of their lives focused on the dental needs of children. They have extensive education and training focused on the Oral health needs of children. Along with knowledge about dental issues, their training includes child psychology and behavior guidance.
Child-Friendly Techniques
Pedodontists aim to make the dental visit feel like an adventure instead of a scary experience. They use gentle, age-appropriate communication styles to engage kids with stories or games. Their office has kid-friendly decor, toys, and rewards to help children feel at ease.
They employ positive reinforcement and sedation techniques for complex procedures. Along with standard preventive and restorative treatments, they also manage common childhood habits. Prolonged thumb sucking or tongue thrusting are seen to have negative oral effects.
